Why an MRI scan is done
MRI scans can be used to:
- find out what's causing any symptoms you've been having
- check your bones and organs
- see how well a treatment is working, for example checking the size of a tumour during and after cancer treatment
Preparing for an MRI scan
The hospital where you're having the MRI scan will tell you if there's anything you need to do before you have the scan.
You may be asked to:
- not wear anything that has metal in it, such as jewellery, a bra, hair clips or hearing aids
- remove coins or keys from your pockets
- change into a hospital gown if your clothes have any metal parts, like zips
- not wear make up
You'll be asked to fill in a form asking if you:
- are pregnant, or may be pregnant
- are breastfeeding
- have had surgery before
- have any kidney problems
- have any metal parts in your body such as surgical clips, a pacemaker, dental fillings or bridges
- have any allergies including to a dye called contrast medium used during some scans
Talk to your GP or healthcare professional at the hospital if you're feeling anxious about having an MRI scan or have a fear of small spaces (claustrophobia). You may be able to have a medicine to help you relax.
You can also ask if you can bring someone to support you during the scan.
What happens during an MRI scan
An MRI scan is done in hospital by a healthcare professional called a radiographer.
It usually takes between 15 minutes and 1 hour, but can take longer.
Before an MRI scan
At your scan appointment, you may be given an injection with a contrast medium (dye) to help show more detail in the MRI scan pictures.
During an MRI scan
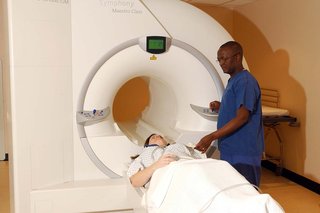
During an MRI scan:
- You'll be asked to lie flat on a bed.
- You'll be given ear plugs or headphones to protect your ears because MRI scanners make loud bangs and clicks as they take pictures.
- The radiographer will control the scanner from another room. They'll be able to hear and speak to you during the scan.
- You'll need to lie still so the scanner can take clear images.
- You may be asked to hold your breath during parts of the scan.
After an MRI scan
After your scan, the radiographer will come back into the room to lower the bed so you can get up.
If you were given contrast medium, you may be asked to wait in hospital for up to 30 minutes to make sure you do not have a reaction to it.
If you had a medicine to help you relax during the MRI scan, you may be able to go home within a few hours. Someone will need to collect you from the hospital and take you home by car or taxi as you should not drive for 24 hours.
You'll be able to eat and drink as normal after the scan.
Getting your MRI scan results
It usually takes between 1 and 2 weeks for you to get your MRI scan results.
The images need to be looked at by a specialist called a radiologist.
They will write to the doctor who referred you for the scan. You may need a follow-up appointment to talk about your MRI scan results.
If you have not heard anything after a few weeks, contact the doctor who referred you for the scan.
The doctor should talk to you about your results and explain what happens next. Tell them if you have questions about your results, or do not understand them.
Possible complications of an MRI scan
An MRI scan is a common procedure. Serious complications are rare.
If you had an injection of contrast medium (dye), you may get a small bruise in the area where you had the injection.
The contrast medium may cause side effects, but these are usually mild and should not last very long. Side effects may include:
- feeling or being sick
- a skin rash
- a headache
- a metallic taste in your mouth
- feeling dizzy
Allergic reactions to the contrast medium are rare, but can include:
- coughing, wheezing or sneezing
- fainting
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- a rash, hives or itchy red skin
Most reactions happen soon after or within the first hour of having contrast medium. Tell the radiographer if you start to feel unwell during or after the scan.
You'll be asked to wait at the hospital for around 30 minutes after having the scan to check for any reaction to the contrast medium.
Page last reviewed: 11 September 2025
Next review due: 11 September 2028