Symptoms of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can feel like a bad cold or flu. The tonsils at the sides of your throat will be red and swollen.
Symptoms in children and adults can include:
- a sore throat
- problems swallowing
- a high temperature
- coughing
- a headache
- feeling and being sick
- earache
- feeling tired
Sometimes the symptoms can be more severe and include:
- swollen, painful glands in your neck (feels like a lump on the side of your neck)
- pus-filled spots or white patches on your tonsils
- bad breath
What your tonsils may look like if you have more severe symptoms of tonsillitis
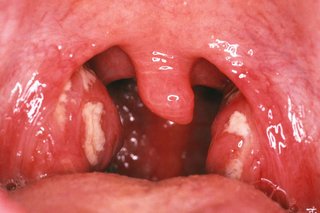
If you're not sure it's tonsillitis
These symptoms are common and can be caused by other conditions. Find out about other causes and treatments for sore throat symptoms.
How long tonsillitis lasts
Symptoms of tonsillitis usually go away after 3 to 4 days but can last longer.
Tonsillitis is not contagious but most of the infections that cause it are contagious, for example colds and flu.
To stop these infections spreading:
- if you or your child have a high temperature or you do not feel well enough to do your usual activities, try to stay at home and avoid contact with other people until you feel better
- use tissues when you cough or sneeze and throw them away
- wash your hands after coughing or sneezing
How to treat tonsillitis yourself
Tonsillitis usually gets better on its own after a few days but it can last longer.
To help treat the symptoms:
- get plenty of rest
- drink cool drinks to soothe the throat
- take paracetamol or ibuprofen (do not give aspirin to children under 16)
- gargle with warm salty water (children should not do this)
How to gargle with salty water
- Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and stir until it has dissolved.
- Gargle with the salty water (do not swallow it), then spit it out.
- Repeat as often as you like.
Young children should not gargle with salty water.
A pharmacist can help with tonsillitis
Speak to a pharmacist about tonsillitis.
They can give advice and suggest treatments, like:
- lozenges containing a local anaesthetic, antiseptic, or anti-inflammatory medicine
- throat sprays (although there's little proof they help)
- antiseptic solutions
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- the symptoms of tonsillitis do not go away within 1 week
- you keep getting throat infections
Urgent advice: Get help from NHS 111 now if:
- you have pus-filled spots on your tonsils
- you have a sore throat so painful it's difficult to eat or drink
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
What happens at your GP appointment
A doctor can usually tell if it's tonsillitis by asking about your symptoms and looking in your throat.
You may also need:
- a swab test to see if bacteria are causing your tonsillitis (a cotton bud is used to wipe the back of your throat)
- a blood test for glandular fever if symptoms are severe or will not go away
Treatment from a GP for tonsillitis
Treatment for tonsillitis will depend on what's causing it:
- most children and adults get viral tonsillitis (caused by a virus), which clears up on its own
- for bacterial tonsillitis (caused by bacteria), a GP may prescribe antibiotics
A GP will usually wait for the test results to tell which type you have.
Important: Surgery to remove your tonsils
It's very rare that someone needs to have their tonsils taken out.
This is usually only done if you have severe tonsillitis that keeps coming back.
Causes of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is usually caused by a virus, such as a cold, but it can also be due to a bacterial infection such as strep throat.
Complications of tonsillitis (quinsy)
Complications of tonsillitis are very rare.
Sometimes you can get an area filled with pus (abscess) between your tonsils and the wall of your throat. This is called quinsy.
Immediate action required: Call 999 or go to A&E if:
- you have a severe sore throat that quickly gets worse
- you have swelling inside the mouth and throat
- you have difficulty speaking
- you cannot swallow
- you have difficulty breathing
- you have difficulty opening your mouth
These are signs of quinsy.
Do not drive to A&E. Ask someone to drive you or call 999 and ask for an ambulance.
Bring any medicines you take with you.
Page last reviewed: 08 March 2024
Next review due: 08 March 2027