Boils
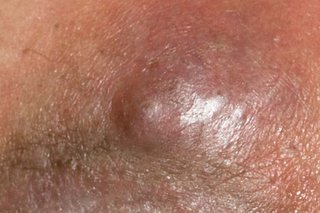
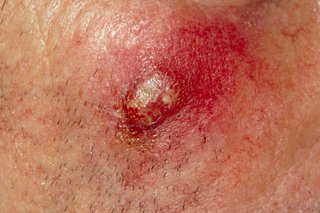
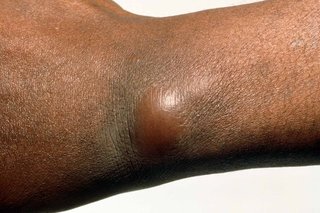
A boil is a hard and painful lump that fills with pus. Most boils go away on their own. See a GP if you keep getting them.
Symptoms of a boil
Things you can do to help boils
There are things you can do to treat boils yourself and stop them coming back.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- you've had a boil for 2 weeks and the things you've tried are not helping
- you keep getting boils
- you have a group of boils (carbuncle)
Urgent advice: Ask for an urgent GP appointment or get help from NHS 111 if you have a boil and:
- it is on your face
- the skin around your boil feels hot, painful and swollen
- you feel hot, cold or shivery
- you have a weakened immune system – this could be from taking treatments such as steroids, or having a condition like diabetes
You can call 111 or get help from NHS 111 online.
Treatment for boils
A GP can check if you need treatment.
You may need:
- a small procedure to drain the boil to get rid of the pus
- antibiotics
Causes of boils
You may be more likely to get boils if you have a long-term condition that affects your immune system, such as diabetes or HIV.
You may also be more likely to get boils if:
- you're a man
- you've been in close contact with someone with boils
- you have certain skin conditions, such as eczema
- you take certain medicines, such as steroids
- you’re living with obesity or malnutrition
Carbuncles are less common and mostly affect middle-aged men.
Page last reviewed: 20 June 2023
Next review due: 20 June 2026